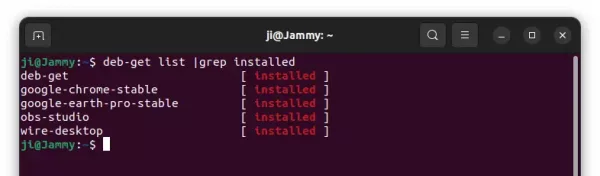
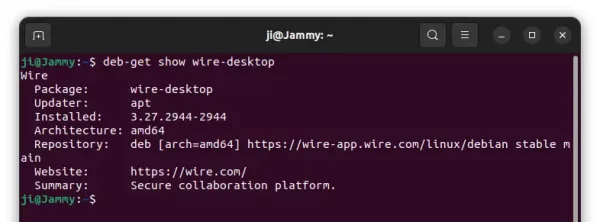
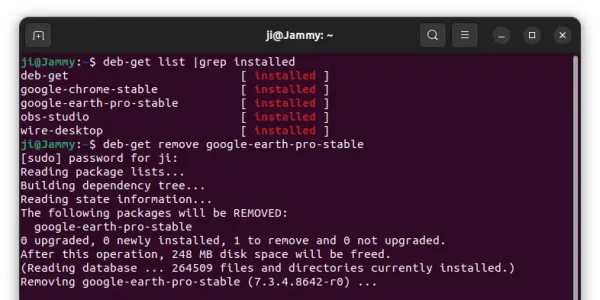
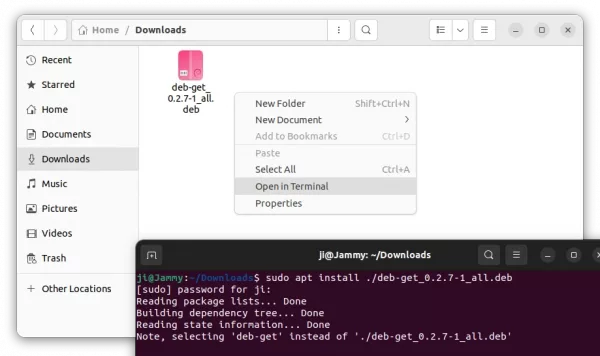
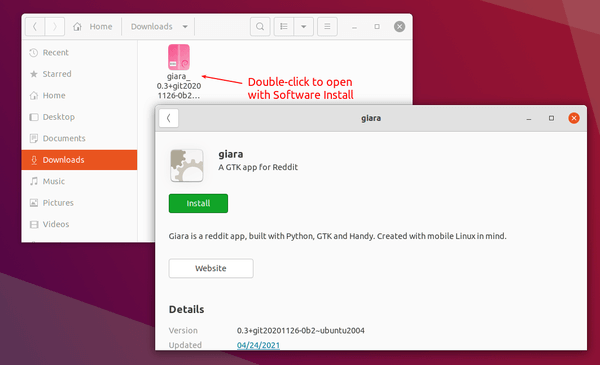
Since Ubuntu 23.10, there’s no longer “Software Install” option for opening/installing .deb files in your Downloads folder. This is probably due to switch to the new ‘App Center’, that some features are not fully implemented.
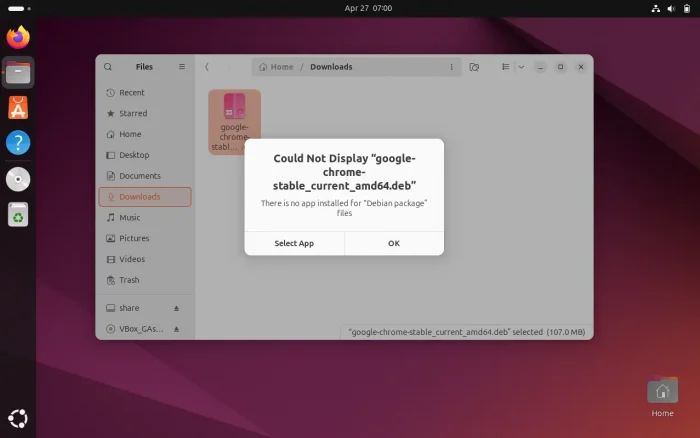
When you double-clicking a .deb file from Downloads folder, it will pop-up a dialog saying “Could Not Display ‘file_name.deb’ There’s no app installed for ‘Debian package’ files“. And, neither option will work for installing the package.
UPDATE: App Center in Ubuntu 24.04 finally added back the feature to install local .deb! Just double-click on the package in file manager to launch and install.
So, if you’re trying to install an application using local .deb format package, here are 3 workarounds for you.
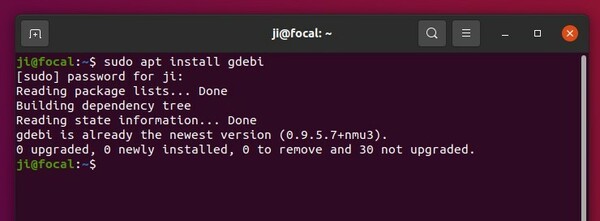
Option 1: use Gdebi package installer
Gdebi is a simple tool to view and install local .deb file. It’s a popular application that’s using as default in Linux Mint.
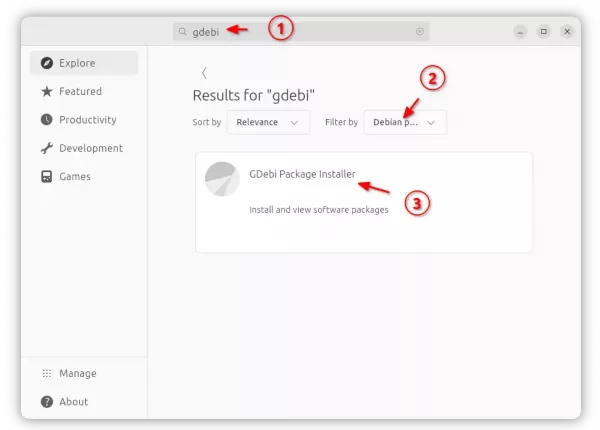
1. First, press Super (Windows logo) key to open overview screen. Search for and launch “App Center”.
2. When ‘App Center’ opens, use it to search and install Gdebi. You may need to select “Filter by Debian packages” to make it visible.
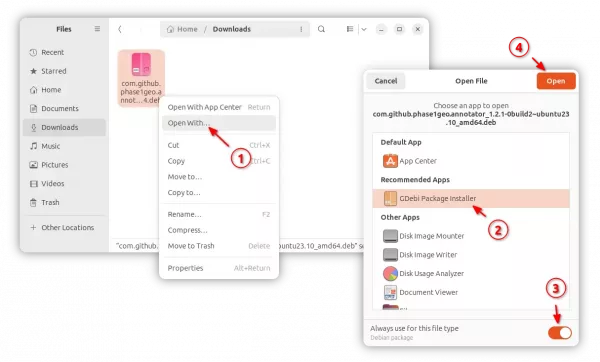
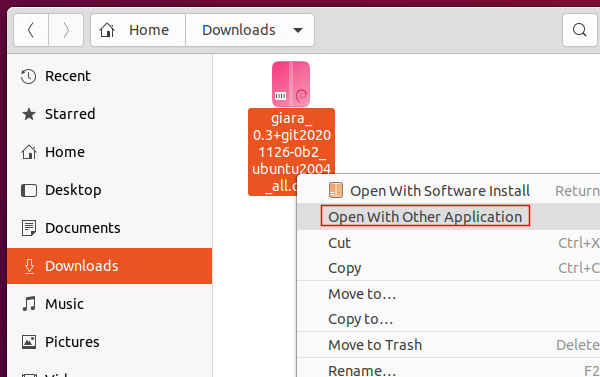
3. Once you installed the tool, right-click on your local .deb file, and click on “Open With…” option.
In next pop-up dialog, find out and select “Gdebi Package Installer” and turn on “Always use for this file type“, finally click Open.
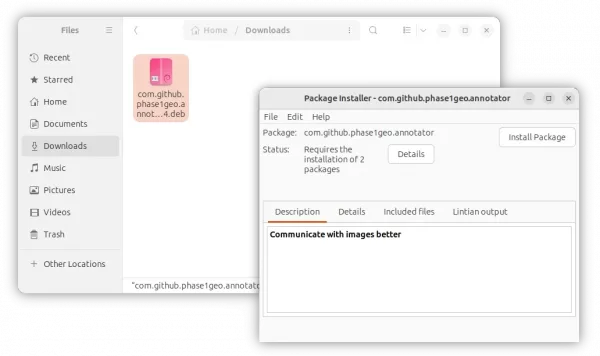
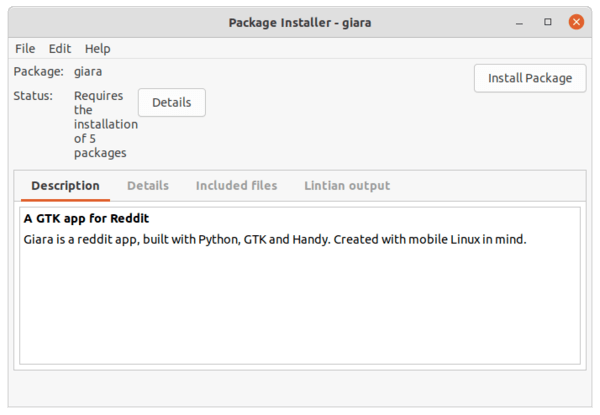
4. After that, you can double-click any .deb file to open with the Gdebi package installer. When the tool opens, you may view the package info and click “Install Package” to install it into your system.
Option 2: Use apt command
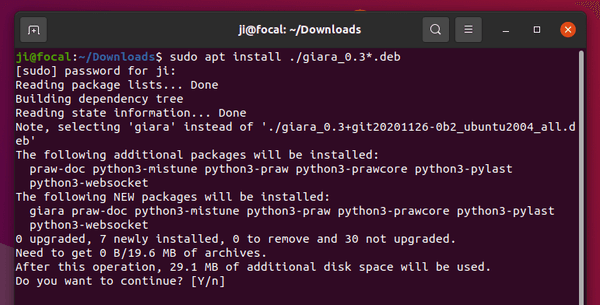
For those who are familiar with Linux command, your local .deb file is easy to install via a single command.
It’s:
sudo apt install /path/to/file.deb
Definitely, you need to replace ‘/path/to/file.deb‘ to yours.
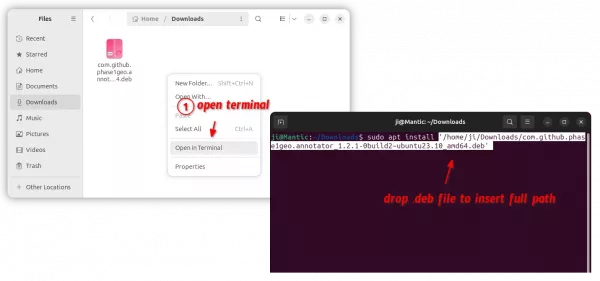
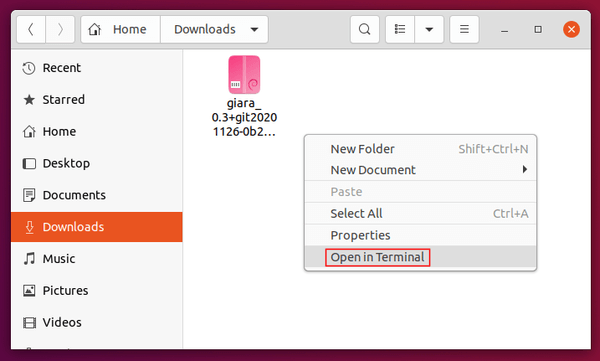
Instead of typing manually, simply open terminal (via either Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut or ‘Open in Terminal’ context menu), then drag and drop .deb file into terminal after typing sudo apt install plus a blank space.
Finally, hit Enter to run the command, type user password (no asterisk feedback) to authentication, and answer y if it asks to confirm.
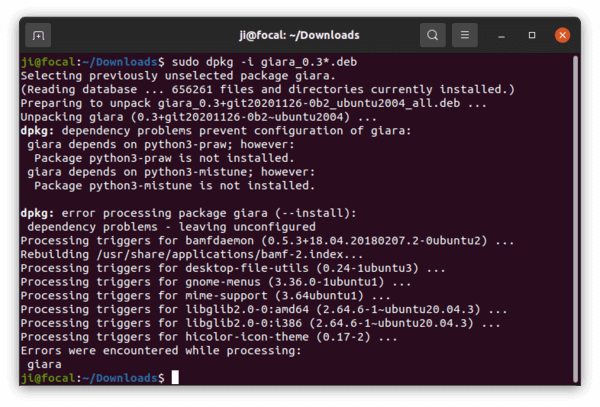
When installation done, it will output something like ‘N: Download is performed unsandboxed as root as file ‘/path/to/file.deb’ couldn’t be accessed by user ‘_apt’. – pkgAcquire::Run (13: Permission denied)’. Just skip the non-fatal warning. Your app should be properly installed when you see the terminal output message.
Option 3: Use GNOME Software
If you want to restore the new App Center to classic Ubuntu Software, then GNOME Software can be a better choice.
GNOME Software supports Deb, Flatpak, and Snap packages. However, it will be always run in background that takes about 200 MB memory in my case.
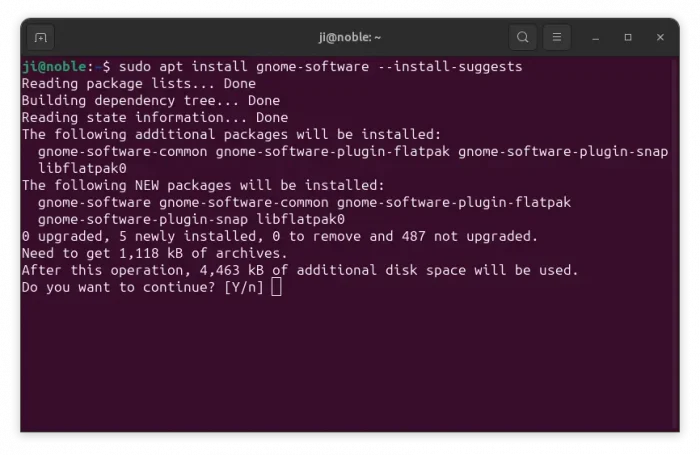
If you don’t care about the memory consumption, then press Ctrl+Alt+T to open terminal, and run command to install GNOME Software:
sudo apt install --install-suggests gnome-software
Skip --install-suggests if you don’t want to enable Flatpak support.
After that, you can right-click on local .deb file, and select “Software Install” from Open With dialog to launch GNOME Software to install it.
Uninstall:
If you don’t use Gdebi or Gnome Software anymore, open terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and run command to uninstall:
Uninstall Gdebi:
sudo apt remove --autoremove gdebi
Or, uninstall Gnome Software via command:
sudo apt remove --autoremove gnome-software