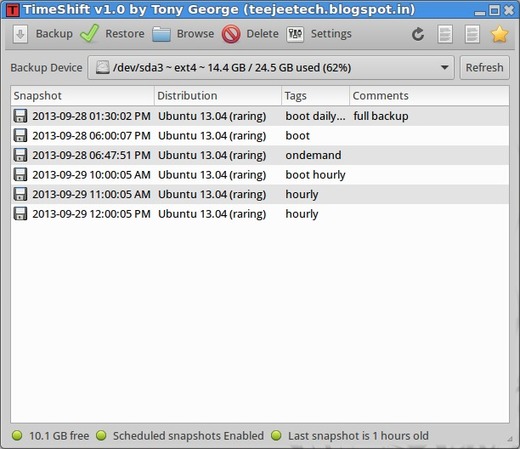
Want to create a Windows like system restore point? Well, TimeShift is the tool, which protects your system by taking incremental snapshots of the file system at regular intervals. These snapshots can be restored later to bring your system to the exact state it was in at the time when the snapshot was taken.
TimeShift is designed to protect only system files and settings. User files such as documents, pictures and music are excluded.
Features:
- TimeShift requires very little setup. Just install it, run it for the first time and take the first snapshot. A cron job will be enabled for taking automatic snapshots of the system at regular intervals. The backup levels can be selected from the Settings dialog.
- Snapshots are saved by default on the system (root) partition in path /timeshift. Other linux partitions can also be selecte
- Boot snapshots provide an additional level of backup and are taken 30 minutes after the system is started.
- Hourly, daily, weekly and monthly levels can be enabled if required.
- TimeShift runs at regular 30-minute intervals but takes snapshots only when needed.
- Applications like rsnapshot rotate a snapshot to the next level by creating a hard-linked copy. Creating a hard-linked copy may seem like a good idea but it is still a waste of disk space. This is because only files can be hard-linked and not directories. The duplicated directory structure can take up as much as 100 MB of space. TimeShift avoids this wastage by using tags for maintaining backup levels. Each snapshot will have only one copy on disk and is tagged as “daily”, “monthly”, etc. The snapshot location will have a set of folders for each backup level (“Monthly”, “Daily”, etc) with symbolic links pointing to the actual snapshots tagged with the level.
- Snapshots can be restored either from the running system or from a live CD. Restoring backups from the running system requires a reboot to complete the restore process.
- You can also TimeShift across distributions. Let’s say you are currently using Xubuntu and decide to try out Linux Mint. You install Linux Mint on your system and try it out for a week before deciding to go back to Xubuntu. Using TimeShift you can simply restore the last week’s snapshot to get your Xubuntu system back. TimeShift will take care of things like reinstalling the bootloader and other details. Since installing a new linux distribution also formats your root partition you need to save your snapshots on a separate linux partition for this to work.
Install TimeShift via PPA:
The PPA is ready for Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04, Ubuntu 22.10 and their derivatives, such as Linux Mint, Elementary OS.
Press Ctrl+ALt+T on your keyboard to open terminal. When it opens, run below commands one by one:
sudo apt-add-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/timeshift sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install timeshift










Nice.
I will try this today on my Dell 3521 laptop :-)