Converseen image converter announced 0.9.10.0 release few days ago. Here’s how to install it in Ubuntu via PPA.
Converseen is a free and open-source tool for converting or resizing a large quantity of photo images to another format with a few mouse clicks.
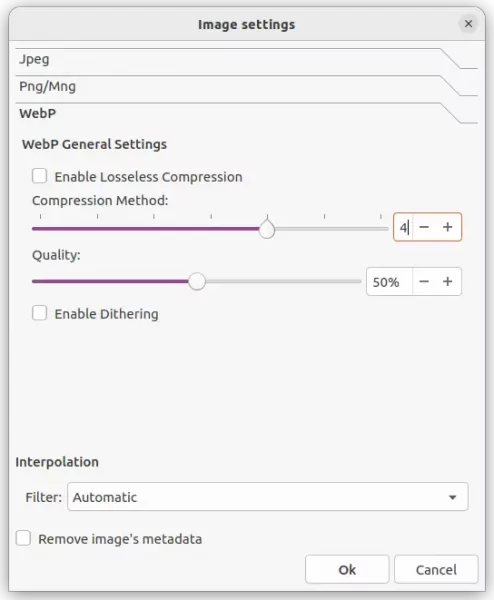
The new 0.9.10.0 release redesigned the Images Settings dialog. Previously, it automatically removes the metadata (information including date & time, device, and even location you capture the photo image) in output images, and replaces with only modified date and other non-sensitive data.
Now, it provides a “Remove image’s metadata” check-box. So, user can manually choose to either to remove the metadata information about the photo images in output files.
As you can see in the screenshot above, it now supports configuring the compression level and image quality for WebP images. As well, it fixes a bug that inhibits the overwrite feature when the Rename option is checked.
How to install the new Converseen 0.9.10.0 in Ubuntu
The image converter is available to install in different package formats: AppImage, Snap, and Deb. Choose either one that you prefer.
1. AppImage
The software website provides the universal AppImage for downloading via the link button below:
It’s a non-install package. Just grab it, right-click and go to ‘Properties’ dialog to add executable permission. Finally, click run the AppImage will launch the tool.
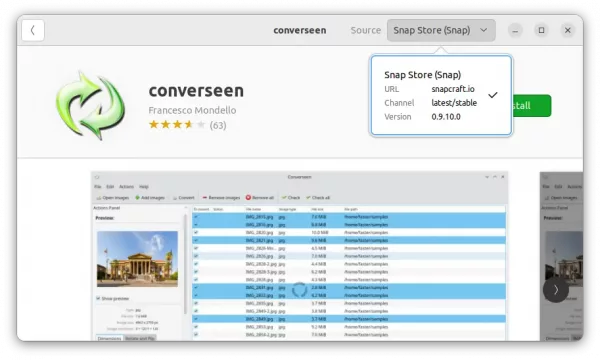
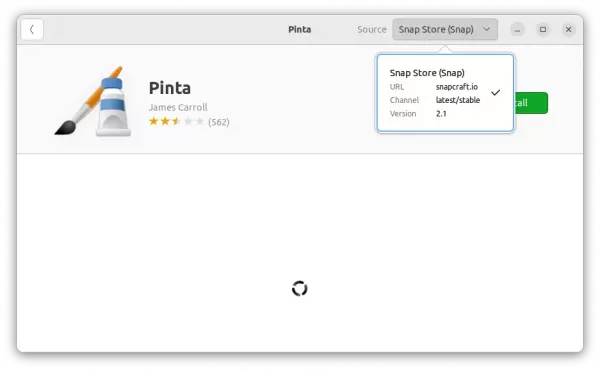
2. Snap
For Ubuntu 20.04+, the snap package is the easiest way to get converseen, though it runs in sandbox. Just open Ubuntu Software, search for and install the package marked as ‘Snap Store (snap)’.
3. Ubuntu PPA (.deb)
For those who prefer the classic .deb package format, there’s unofficial PPA that contains the package for Ubuntu 18.04, Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04, and Ubuntu 22.10.
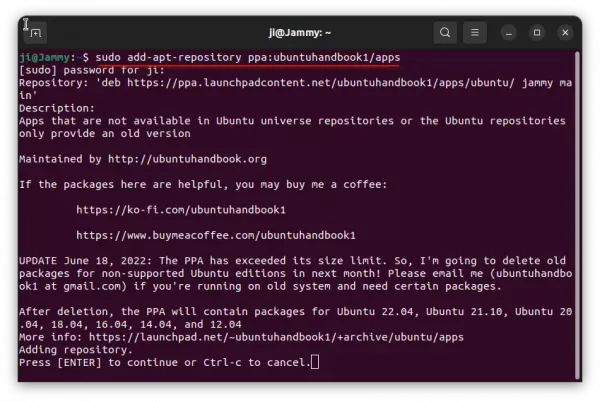
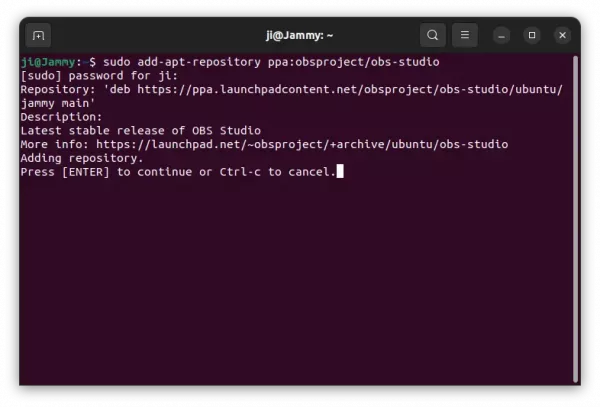
1. First, press Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard to open terminal. When it opens, run command to add the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntuhandbook1/apps
Type user password (no asterisk feedback) and hit Enter to continue.
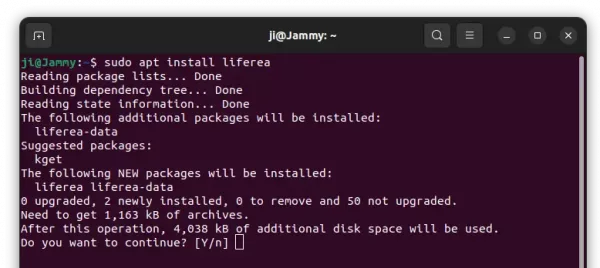
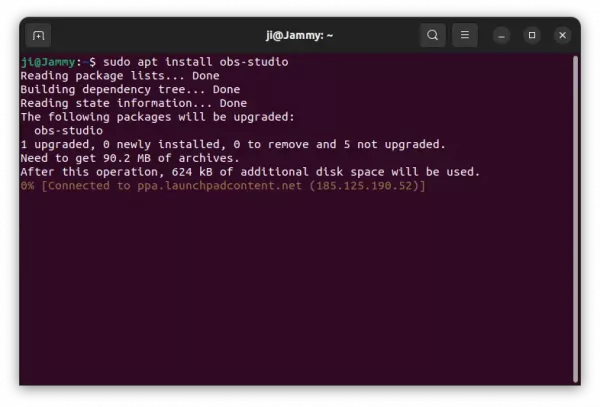
2. Then, install the software package by running command:
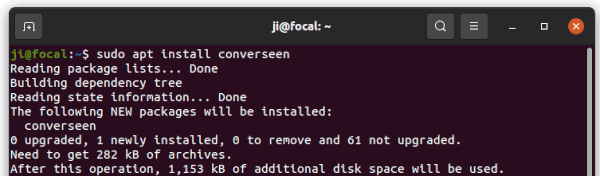
sudo apt install converseen
Linux Mint user may have to run sudo apt update first to update cache.
Uninstall:
The PPA also contains some other software packages, so you may remove it immediately after installed Liferea.
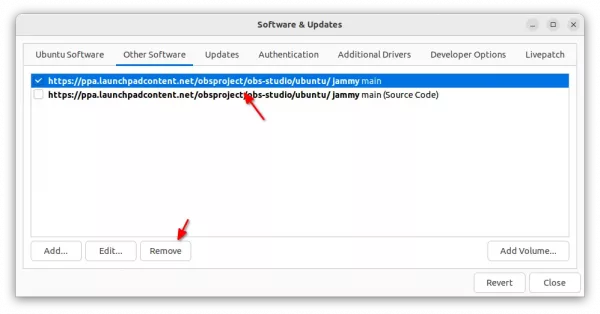
To do so, either run the command below in terminal, or remove the source line under “Other Software” tab in Software & Updates tool.
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:ubuntuhandbook1/apps
To remove the feed reader package, simply run command:
sudo apt remove converseen
That’s all. Enjoy!