This simple tutorial shows how to install the latest Intellij IDEA 2025.1 in Ubuntu 22.04 and Ubuntu 24.04.
IntelliJ IDEA 25.01 was released on April 16, 2025. See the release note for the new features.
The highlights of this release include full Java 24 support, the introduction of Kotlin notebooks and K2 mode enabled by default, marking a major step toward delivering the best Kotlin experience. Additionally, JetBrains AI has received a significant upgrade, …
Intellij IDEA is available to install in Ubuntu via different ways. They include:
- Snap,
- Flatpak,
- official tarball,
- and Ubuntu PPA.
Choose either one that you prefer.
Method 1: Install Intellij IDEA via Snap package
JetBrains provides official Linux package through both Snap and tarball. Which is super easy to install for Ubuntu users.
The Snap package Features:
- Official package by JetBrains.
- Run in sandbox environment.
- amd64 (x86_64) only.
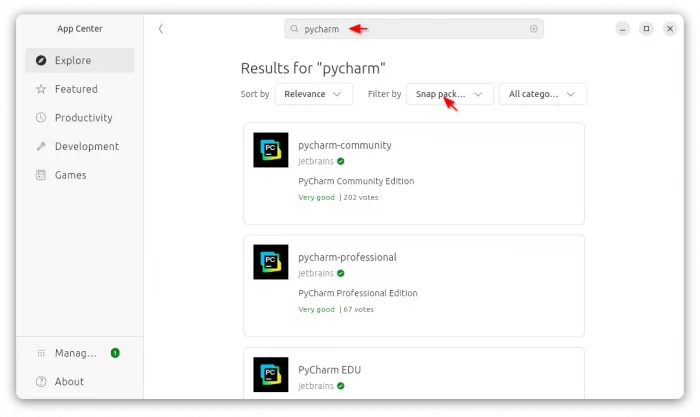
For all current Ubuntu releases, just launch Ubuntu Software (or App Center), then search and install ‘Intellij IDEA Community, or Ultimate’.
For choice, you may press Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard to open terminal, and run command instead the install the Snap package:
snap install intellij-idea-community --classic
The snap package installs updates automatically. You can check (and install if any) updates manually by running command:
snap refresh intellij-idea-community
While, in the commands above replace community with ultimate for the ultimate edition.
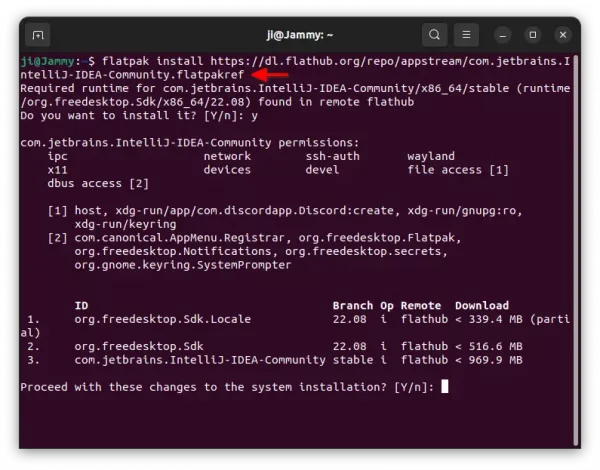
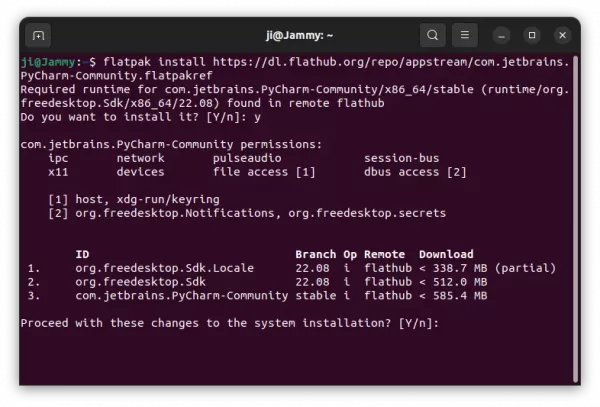
Method 2: Install Intellij IDEA via Flatpak package
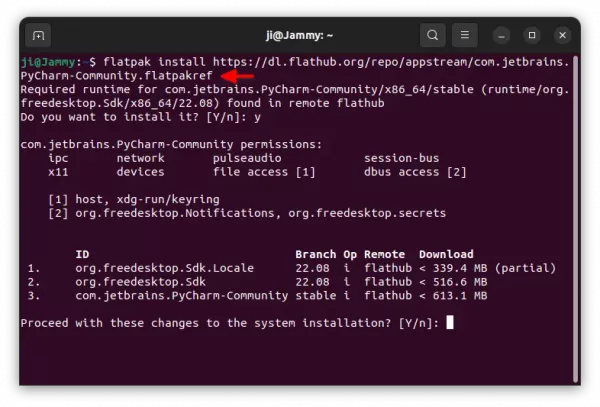
Another easy way to install the IDE is using Flatpak package. Which works in most Linux, though also run in sandbox environment.
The Flatpak package Features:
- Community maintained.
- Run in sandbox.
- amd64 (x86_64) and arm64 support.
Ubuntu users just need to press Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard to open terminal. Then run the 2 commands below one by one to install the package.
And, if you’re first time installing app as Flatpak, log out and back in for the app icon visible in system app launcher.
To update the Flatpak package, use command:
flatpak update com.jetbrains.IntelliJ-IDEA-Community
Method 3: Install IntelliJ IDEA via Official Tarball
If you don’t like or have issue for the IDE running in sandbox, then use the official Linux tarball instead!
The Linux Tarball Features:
- Official package by JetBrains.
- Portable, no installation required.
- amd64 (x86_64) and arm64 support.
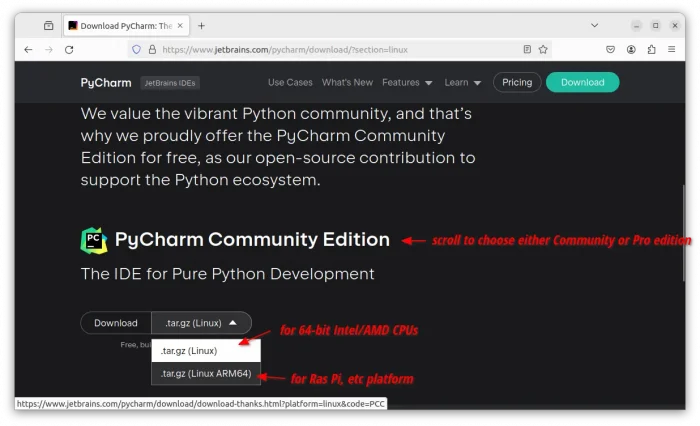
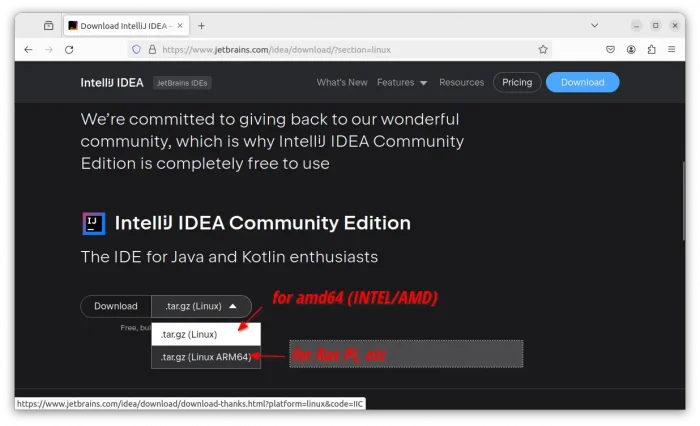
1. First, go to the official download page via the link below:
Depends on your need, either download the Ultimate, or scroll down and select the Community edition. For ARM64, click the down arrow (▿) icon to select from drop-down menu.
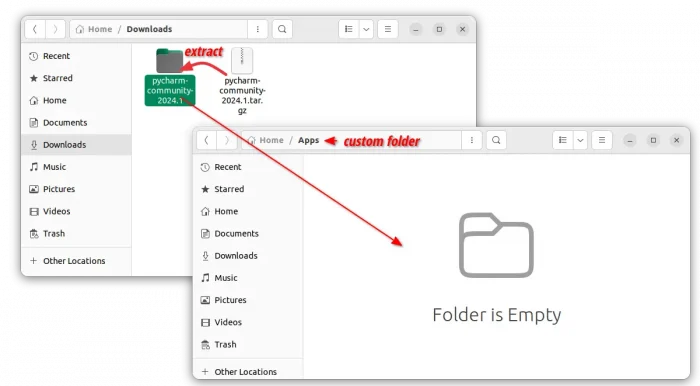
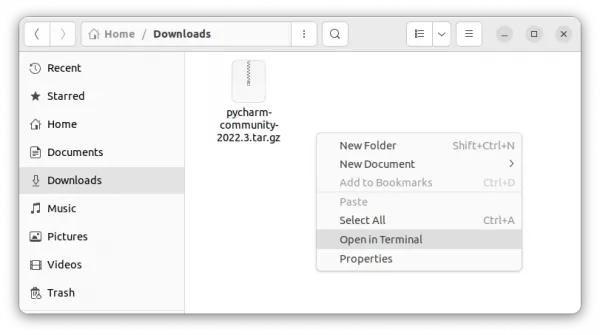
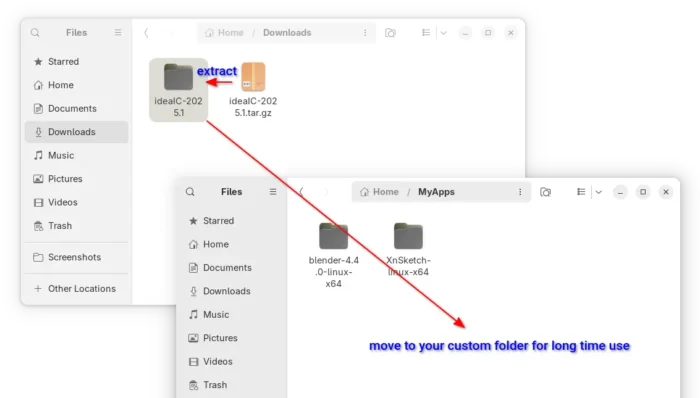
2. After downloaded the tarball, just extract and move the source folder to any location that you want for long time use.
In my case, I created a “MyApps” folder in user home, and put IDEA source folder into it as sub-directory.
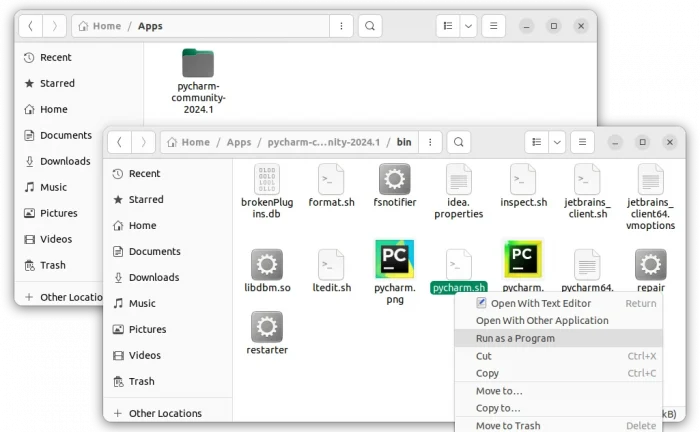
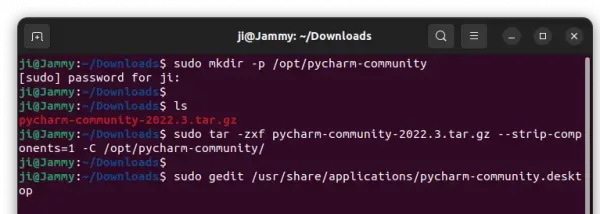
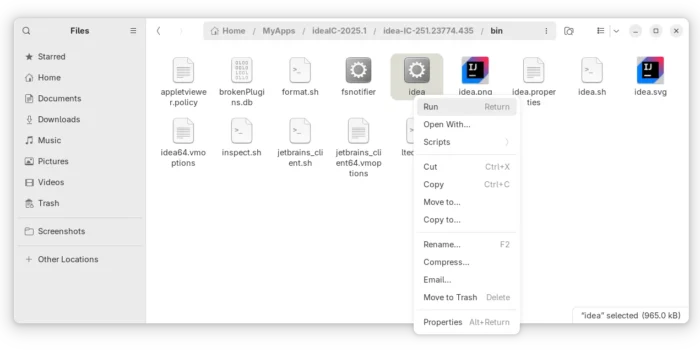
3. Without installation, you can now go to the ‘bin‘ sub-folder, right-click on “idea.sh” and select “Run as Program” to launch the IDE.
4. Create app shortcut, so to launch from start/application menu.
- First, launch text editor and create an empty document.
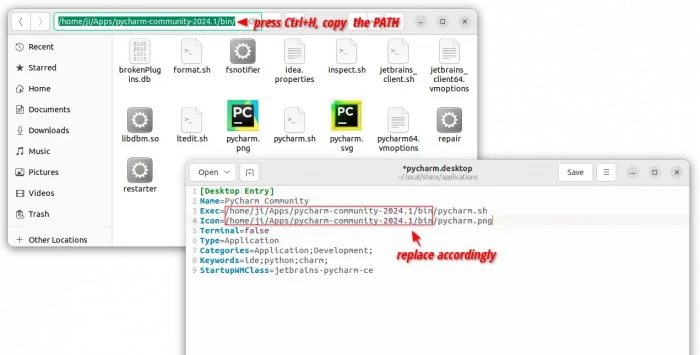
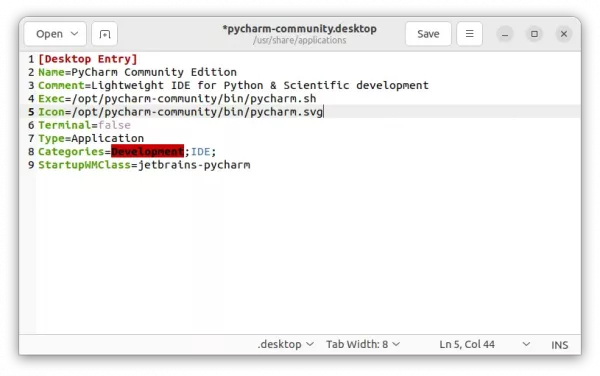
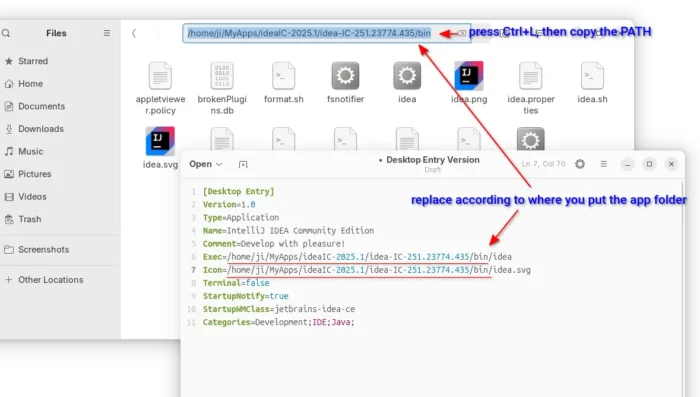
- Then, paste the following lines, and replace “/PATH/TO/IDEA” according to where you put the app folder.
[Desktop Entry]
Version=1.0
Type=Application
Name=IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition
Comment=Develop with pleasure!
Exec=/PATH/TO/IDEA/bin/idea
Icon=/PATH/TO/IDEA/bin/idea.svg
Terminal=false
StartupNotify=true
StartupWMClass=jetbrains-idea-ce
Categories=Development;IDE;Java;
Tips: you may navigate to the ‘bin’ sub-folder of the IDE folder, then press Ctrl+L and copy the path!
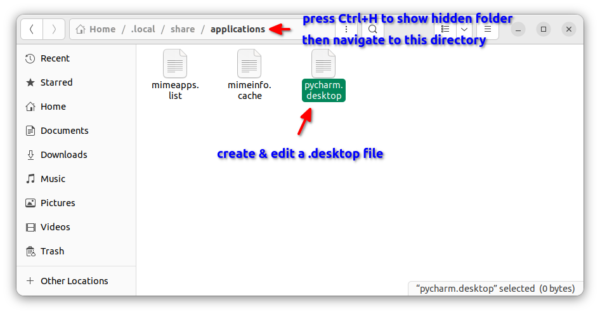
- Finally, save the file as custom_file_name.desktop under
.local/share/applications directory. NOTE: .local is hidden by default, press Ctrl+H to show it.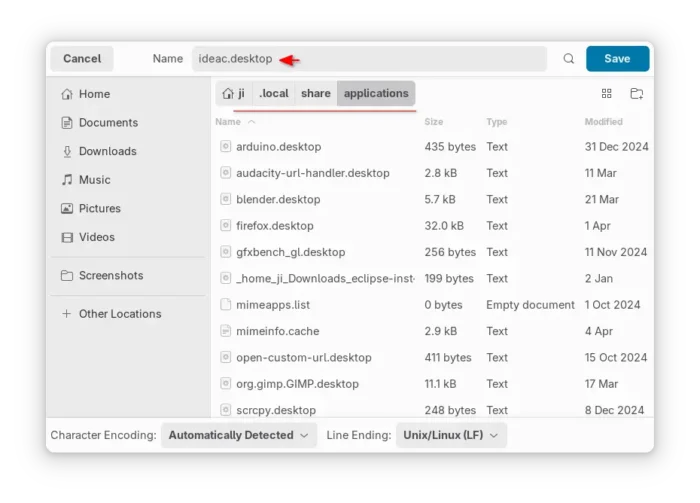
If everything’s done correctly, you can now search for and launch the IDE from app launcher or the overview screen depends on your DE a few moments later:

Method 4: Install IntelliJ IDEA via Ubuntu PPA
Another choice to avoid Snap and Flatpak, is using an Ubuntu PPA. However, there are only third-party maintained PPAs.
As far as I know, there are xtradeb PPA and Marcel Kapfer’s PPA are keeping updated with the most recent IDE packages:
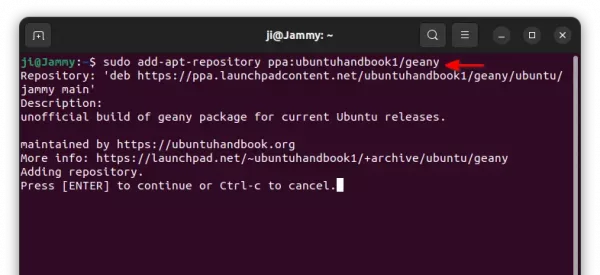
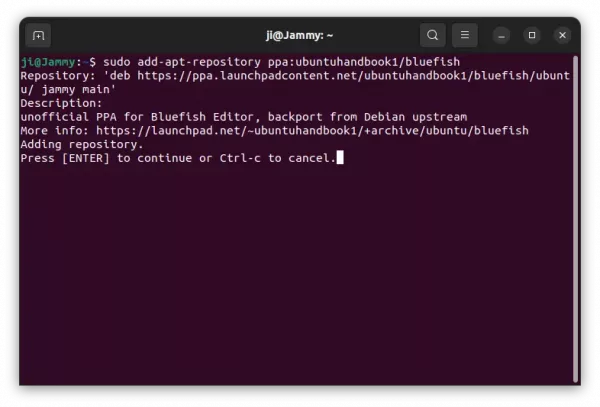
1. Add PPA:
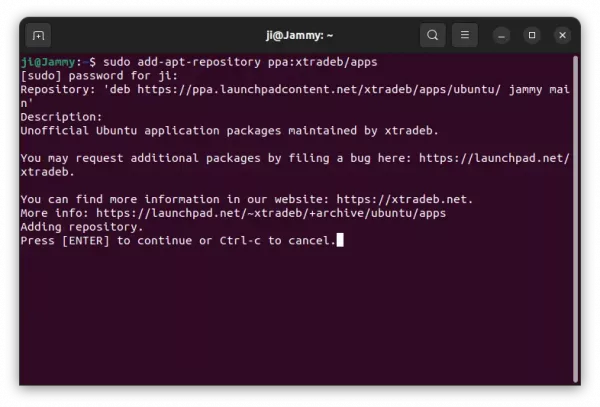
For the xtradeb PPA, so far only support the Community Edition for Ubuntu 24.04 and Ubuntu 25.04 on both amd64 and arm64, use command:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:xtradeb/apps
For Marcel Kapfer’s PPA, that supports both Community and Ultimate editions for Ubuntu 14.04, 16.04, 18.04, 20.04, 22.04, 24.04, 24.10 on amd64, use command:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mmk2410/intellij-idea
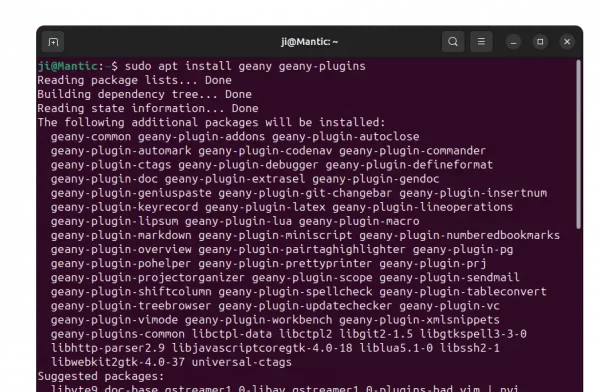
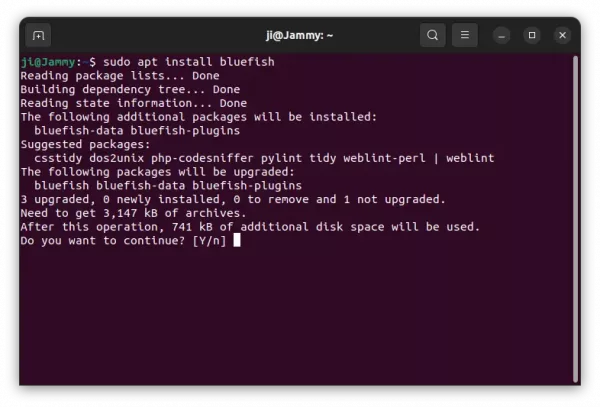
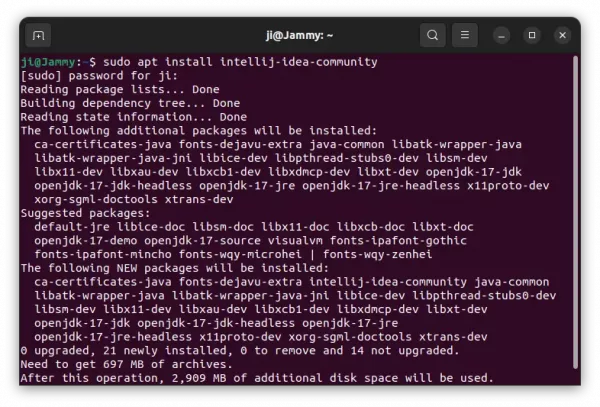
2. Then install the IDE by running command ():
sudo apt install intellij-idea-community
NOTE: Linux Mint user needs to run sudo apt update after adding PPA to manually refresh system package cache.
Uninstall IntelliJ IDEA
For the Snap package, just remove it from Ubuntu Software or App Center.
For the Flatpak package, open terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and run command to remove it:
flatpak uninstall --delete-data com.jetbrains.IntelliJ-IDEA-Community
And, run flatpak uninstall --unused to remove useless run-time libraries.
For IDEA installed via the official Tarball, just remove the source folder as well as .desktop file under .local/share/applications directory.
For the Ubuntu PPA package, open terminal and run command to remove it:
sudo apt remove --autoremove intellij-idea-community
Also remove the Ubuntu PPA by running command:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:xtradeb/apps