Wine 5.17, a new development release of the compatibility layer allows to run Windows apps on Linux and Mac OS, was released with new features and various bug-fixes.
Wine 5.17 release highlights:
- ADVAPI32 library converted to PE.
- Beginnings of an NDIS network driver.
- Still more restructuration of the console support.
- Various bug fixes.
How to Install Wine 5.17 in Ubuntu:
Open terminal either by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard, or by searching for ‘terminal’ from system application menu. When it opens, run following steps one by one.
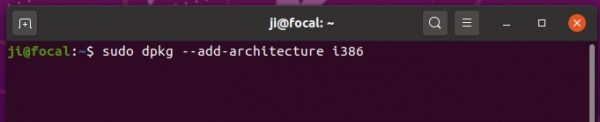
1.) Run command to enable 32 bit architecture (if you haven’t already):
sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386
Type user password (no asterisk feedback) when it asks and hit Enter to continue.
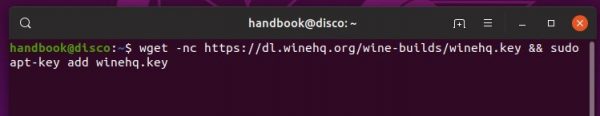
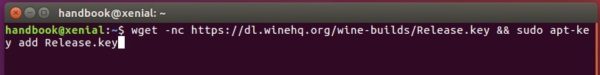
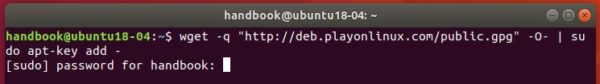
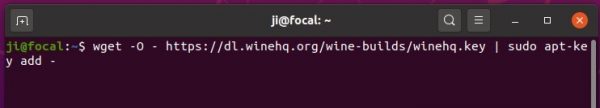
2.) Install the repository key by running command:
wget -O - https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key | sudo apt-key add -
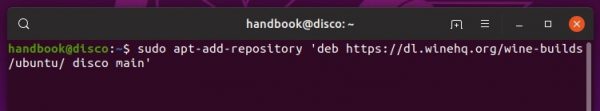
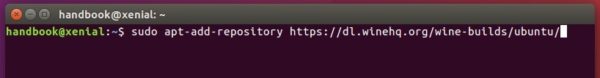
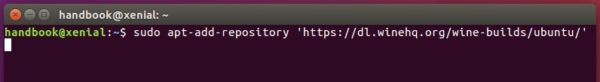
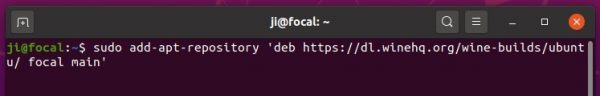
3.) Add wine repository via command (for Ubuntu 20.04 and Linux Mint 20):
sudo apt-add-repository 'deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ focal main'
NOTE: You may replace focal in the code with:
- bionic for Ubuntu 18.04 and Linux Mint 19.x
- xenial for Ubuntu 16.04
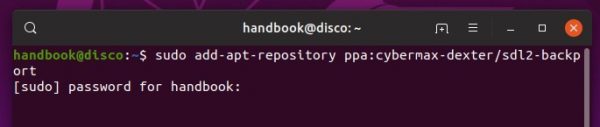
4.) Add PPA for the required libfaudio0 library:
For Ubuntu 18.04 and Linux Mint 19.x only, libfaudio0 library is still required to install from a third-party repository by running command:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cybermax-dexter/sdl2-backport
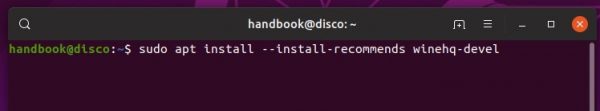
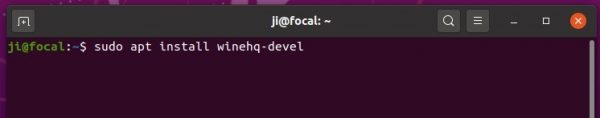
5.) Finally install Wine 5.17 via command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install --install-recommends winehq-devel
NOTE: installing the latest development release will automatically remove the stable version (if installed).
And for the unmet dependencies issue installing 32-bit libraries, try running command:
sudo apt-get install libgnutls30:i386 libldap-2.4-2:i386 libgpg-error0:i386 libxml2:i386 libasound2-plugins:i386 libsdl2-2.0-0:i386 libfreetype6:i386 libdbus-1-3:i386 libsqlite3-0:i386
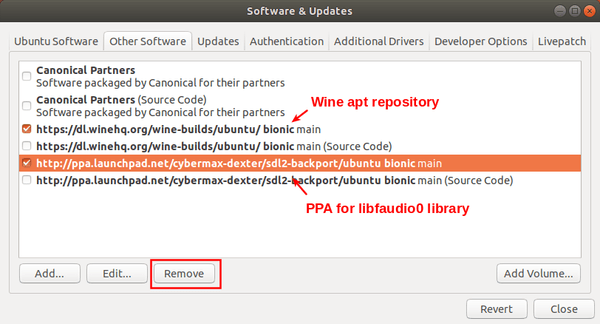
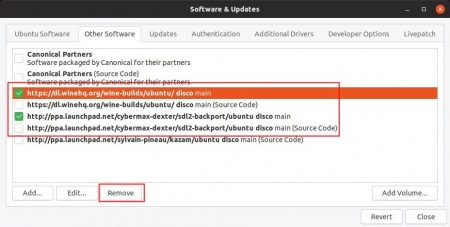
(Optional) After successfully installed Wine 5.17, you may remove the PPAs by launching Software & Updates utility and navigating to Other Software tab.