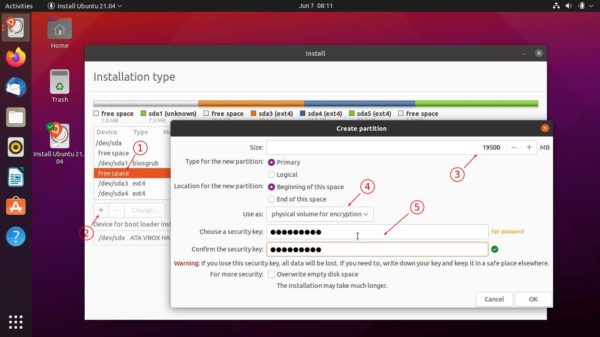
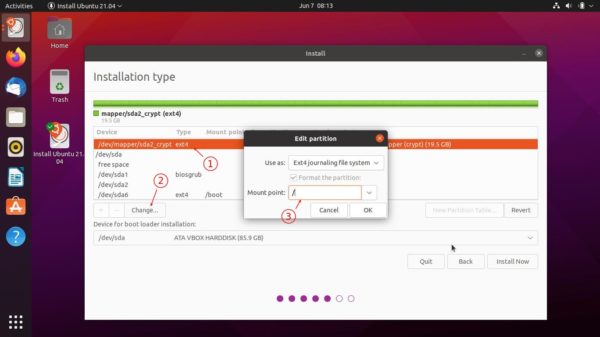
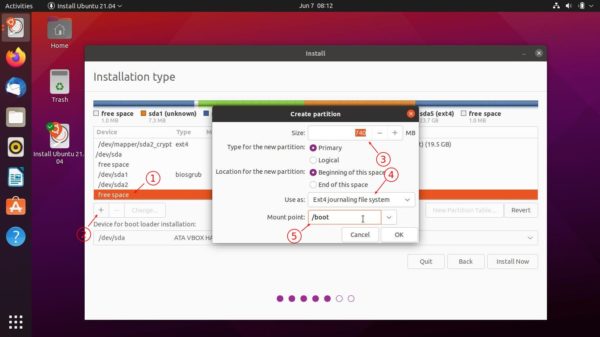
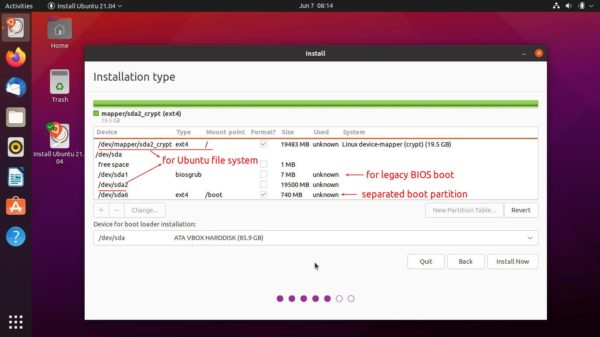
![]()
Ubuntu lists all the available user accounts in the GDM login screen. You can however remove them to protect your privacy.
Gnome, the default desktop environment, has a hidden option to force users to type the username and then password to login. If you’re working on public places, it will be good to enable this option for privacy concern.
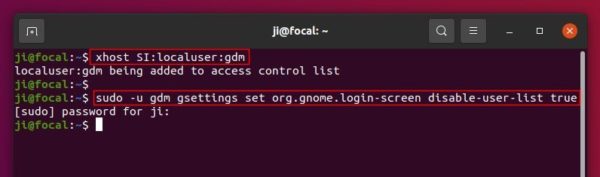
1.) Firstly open terminal either from system app launcher or by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard. Because the login screen is handled by gdm, you have to firstly run command to allows it to make connections to X server.
xhost SI:localuser:gdm
Though it says for X, you also need to run the command in Wayland session to avoid error to disable user list.
2.) Now run gsettings command to disable user list via user gdm:
sudo -u gdm gsettings set org.gnome.login-screen disable-user-list true
Type user password, no asterisk feedback, for sudo prompt and hit Enter.
In next boot, you will no longer see the user accounts. Instead, you need to type username and then password to login.
How to Reset:
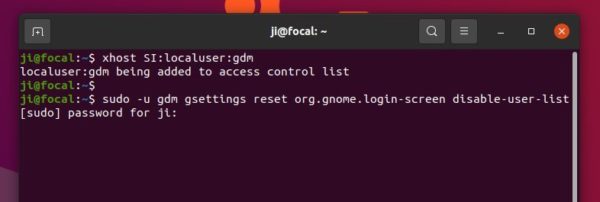
To restore the login screen setting, also run both xhost and gsettings commands in a terminal window.
To be lazy, I’ll combine the two commands into single, so it will be:
xhost SI:localuser:gdm && sudo -u gdm gsettings reset org.gnome.login-screen disable-user-list
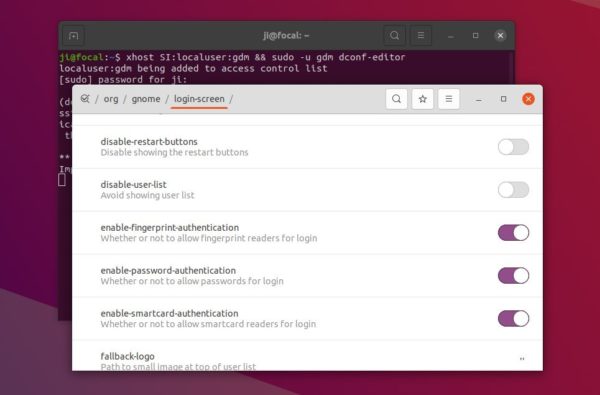
In addition for more Login Screen settings, e.g, disable ‘Power Off’ menu option, toggle authentications, you can open Dconf Editor (install it first from Ubuntu Software) via user gdm:
xhost SI:localuser:gdm && sudo -u gdm dconf-editor