The free cross-platform Deluge BitTorrent client released version 2.1.0 one day ago. Here’s how to install it in Ubuntu 18.04, Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 22.04.
Deluge is a fully-featured torrent downloading app with GTK, web UI, and command line interfaces. The app features protocol encryption, DHT, Local Peer Discovery (LSD), Peer Exchange (PEX), UPnP/NAT-PMP, web seeds, stream torrent and more.
The new 2.1.0 was released with minimum libtorrent requirement increased to v1.2. Python 2 is no longer supported! And, Python 3.6 is the minimum requirement of the programming language.
New features in Deluge 2.1.0 include:
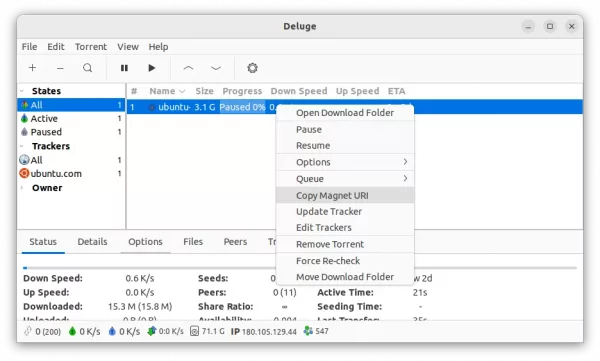
- Add context menu option to copy magnet URI.
- Add support for IPv6 in host lists.
- Add systemd user services, though I didn’t see them in PPA packages.
- Add
is_interfaceandis_interface_nameto validate network interfaces. - Add support for pygeoip dependency for location lookup.
- Add plugin keys to get_torrents_status
- Add support for SVG tracker icons.
- Hide passwords in config logs.
There are as well various bug-fixes, see the release note for details.
How to Install Deluge 2.1.0 in Ubuntu:
The software offers official binary packages for downloading at its website.
For Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Pop! OS, etc, there’s an official Ubuntu PPA contains the packages for Ubuntu 18.04, Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 21.10, Ubuntu 22.04, and other Linux based on them.
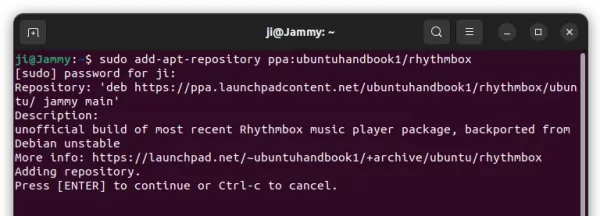
1.) Add the PPA.
Firstly, search for and open terminal from system start menu (“Activities” overview). Or, just press Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut keys on keyboard.
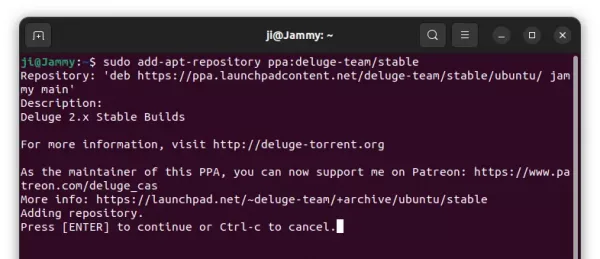
When terminal opens, paste the command below into it and hit Enter to add the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deluge-team/stable
Type user password (no asterisk feedback) when it asks and hit Enter to continue.
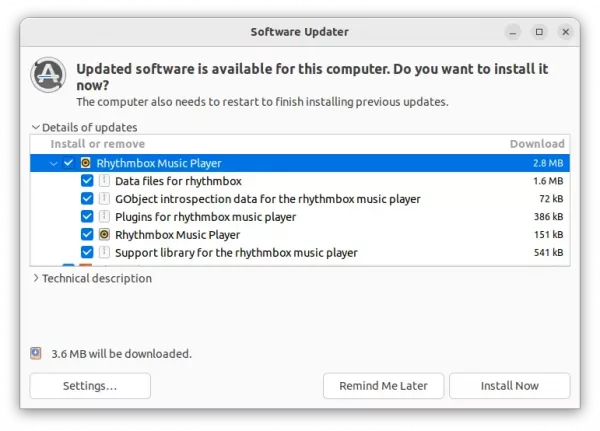
2.) Install / Update Deluge
If you have an old version of the software package installed on your system, simply open “Software Updater” should prompt you the updates of the BitTorrent Client:
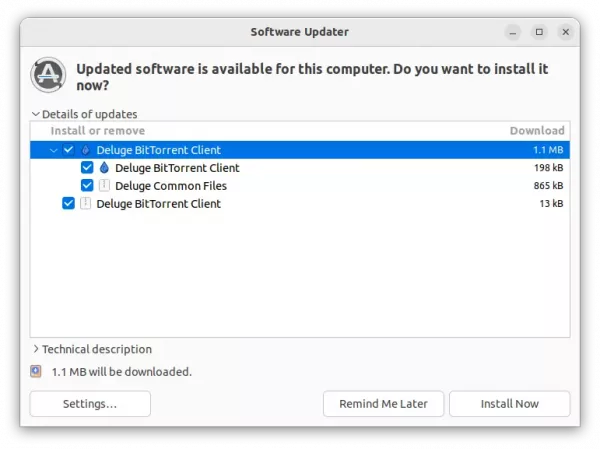
If not, run commands below one by one to refresh package cache and install the software packages:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install deluge
For choice, you may replace deluge with deluged for server, deluge-console for command line interface, or deluge-web for web UI.
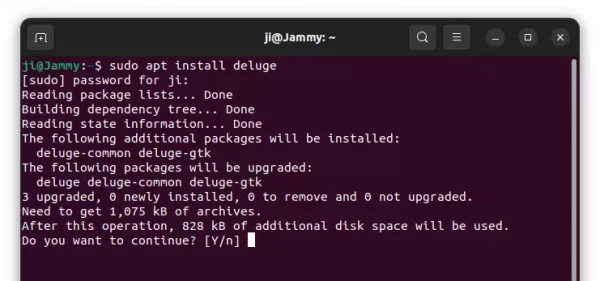
After installation, open the app from system start menu (or search in “Activities” overview) and enjoy!
How to Remove Deluge:
To remove the Ubuntu PPA, either run the command below in a terminal window:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:deluge-team/stable
Or, remove the source line by opening “Software & Updates” utility and navigate to “Other Software” settings tab:
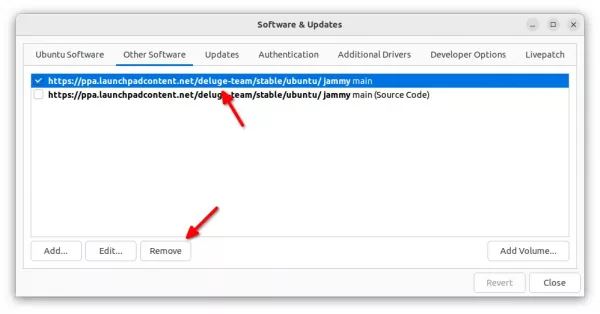
And, remove the torrent client package easily by running command in terminal:
sudo apt remove --autoremove deluge deluge-common
That’s all. Enjoy!