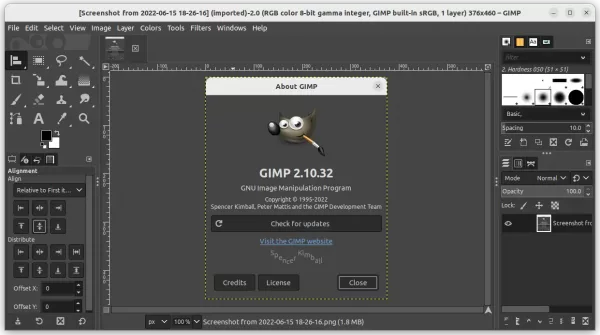
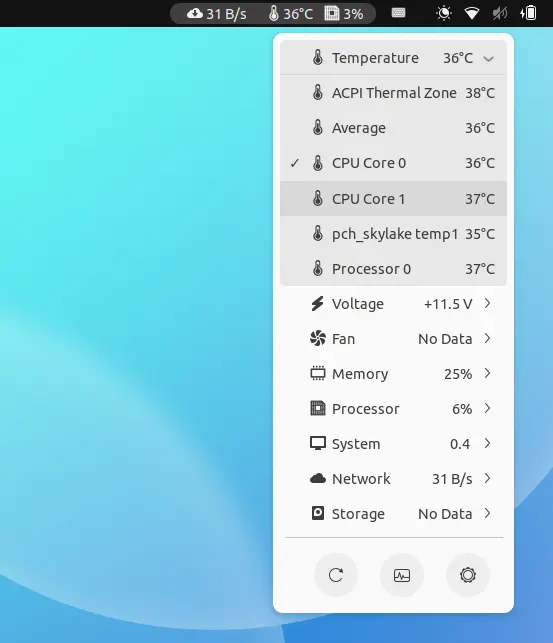
GIMP image editor released a new update for its stable 2.10 release series. Here’s what’s new and how to install in Ubuntu.
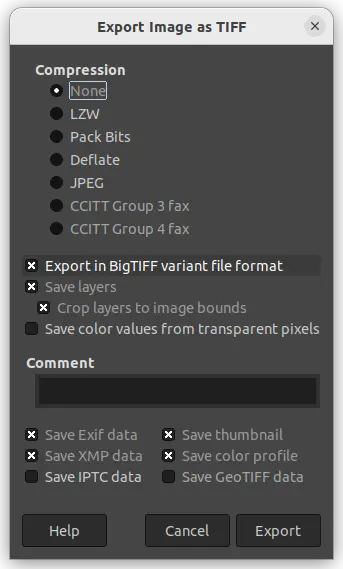
GIMP 2.10.32 comes with BigTIFF file import/export support, which is an evolution of the original TIFF format allowing files bigger than 4GiB. It also supports for importing 8 and 16-bit CMYK(A) TIFF in this release.
The release also backported the JPEG XL file format support from the 2.99.8 development release. It’s so far only has import ability, though a third-party plugin is available with both import and export support.
Other changes include:
- New “Flip the image vertically on export” on DDS export dialog.
- Support loading transparent EPS files
- Improved support of TGA indexed images with alpha channel
- new PDB procedure
file-bmp-save2for plugin developer. - Add localized glyphs (locl) support for Text tool.
- on-hover indicator around the eye and link toggles
- Add “Include mouse pointer” option for Screenshot tool in Windows.
How to Install GIMP 2.10.32 in Ubuntu:
GIMP as Flatpak:
GIMP offers official Linux package via universal Flatpak package.
For, Ubuntu 20.04 and higher, simply press Ctrl+Alt+T to open terminal, and run the command below one by one to install it:
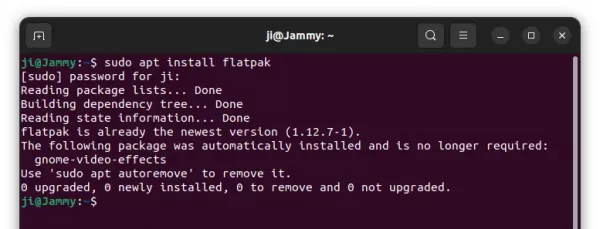
- Install the flatpak daemon via command:
sudo apt install flatpak
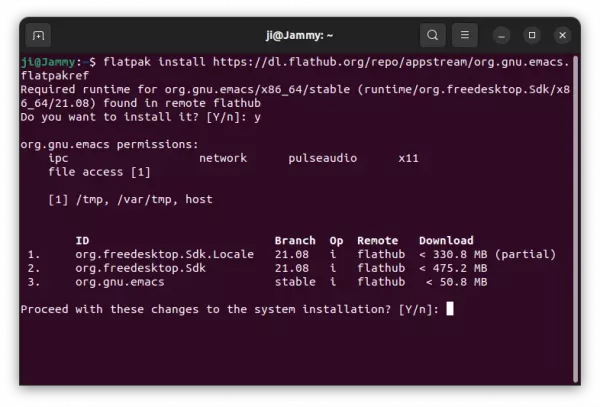
- Then install GIMP via Flatpak using command:
flatpak install https://dl.flathub.org/repo/appstream/org.gimp.GIMP.flatpakref
Ubuntu PPA:
For those do not like sandboxed applications, I’ve uploaded the new release package into this unofficial PPA for Ubuntu 22.04, Ubuntu 21.10, and Ubuntu 20.04 with amd64 and arm64/armhf CPU architecture types support.
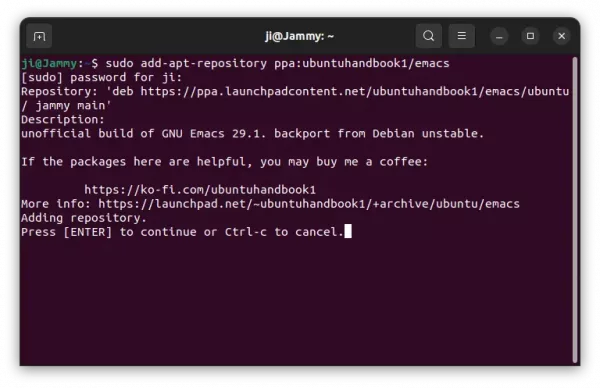
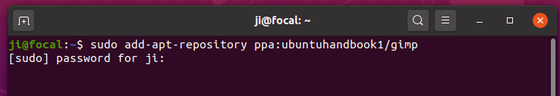
1. First, press Ctrl+Alt+T on keyboard to open terminal. Then run command to add the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntuhandbook1/gimp
Type user password (no visual feedback) when it asks for sudo authentication and hit Enter to continue.
2. Then, refresh system package cache by running command:
sudo apt update
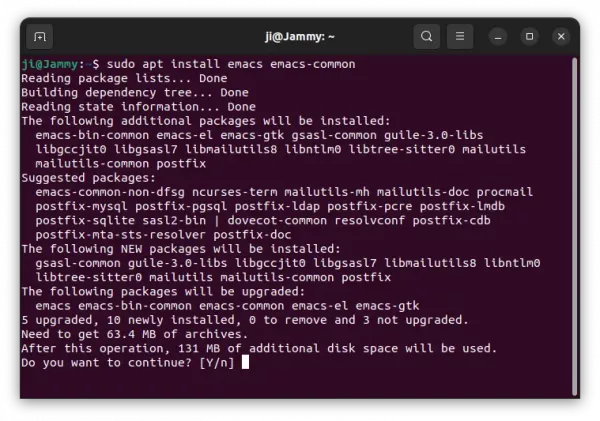
3. And, finally install or update GIMP using command:
sudo apt install gegl gimp
Or, upgrade GIMP image editor via Software Updater after adding the PPA repository:
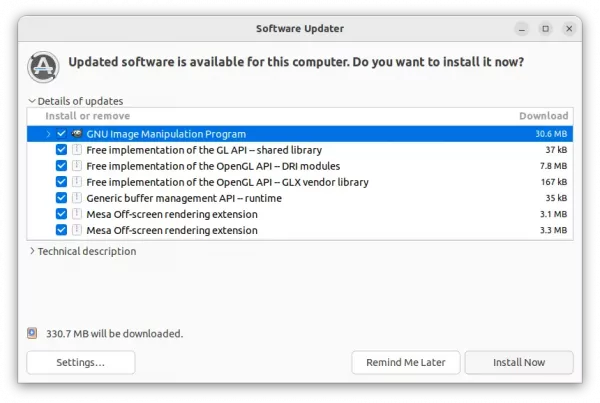
NOTE: Due to build failure of libjxl library for arm64. The official JPEG-XL plugin is excluded in this PPA for Ubuntu 20.04. You can however run the command below to install the third-party plugin mentioned above to get .jxl file import/export support.
sudo apt install libjxl-gimp-plugin