![]()
For those prefer installing app via apt method, there’s now an Ubuntu PPA that contains the latest VLC 3.0.12 deb packages.
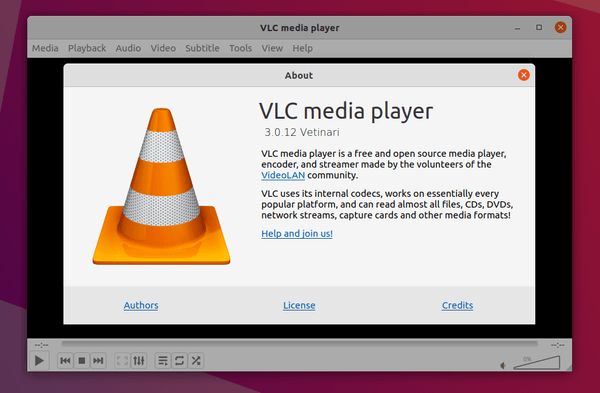
VLC 3.0.12 was released a few weeks ago. It features native Apple Silicon support, RIST protocol, YouTube & Vocaroo scripts updates, and various bug-fixes.
The VideoLAN team offers the official Snap package which can be installed directly from Ubuntu Software. If you don’t like the Snap package however, you can now install the media player from the unofficial PPA.
1.) Add the VLC PPA:
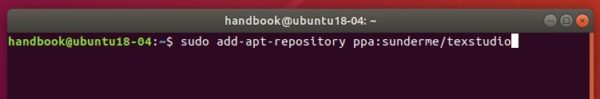
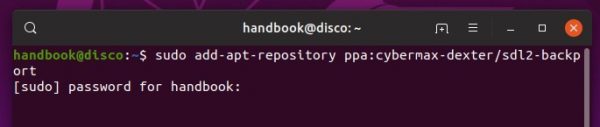
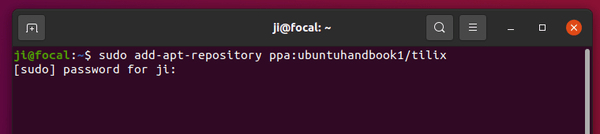
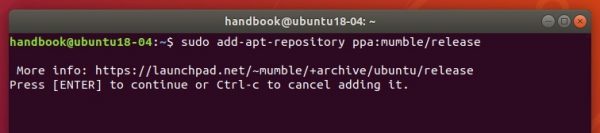
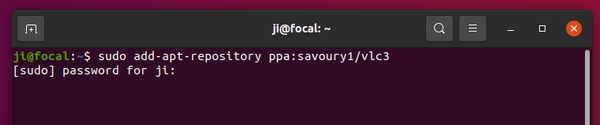
Firstly open terminal from system app launcher. When it opens, run command to add the PPA:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:savoury1/vlc3
Type user password when it asks, while no asterisk feedback, and hit Enter to continue.
For the MATE desktop users, run this command instead to add another PPA with patch from full-screen issue:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:savoury1/vlc3-mate
2.) Add the dependency PPA:
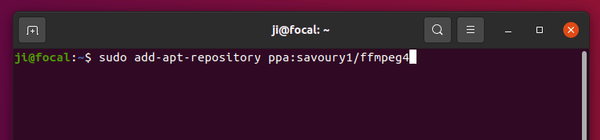
Secondly, add the dependency PPA for updated media tools:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:savoury1/ffmpeg4
3.) Install or update VLC:
Finally, either run command to install VLC media player:
sudo apt install vlc
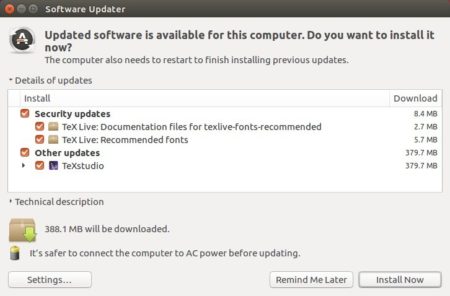
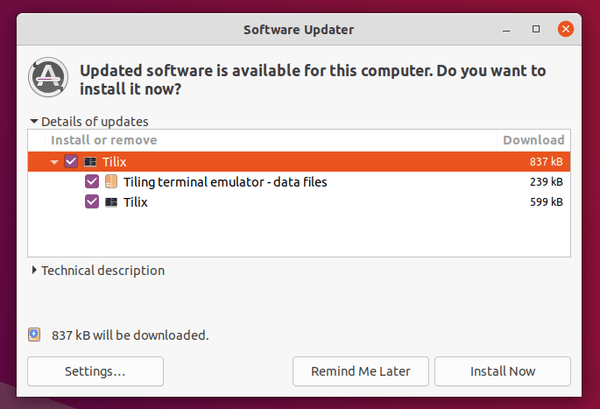
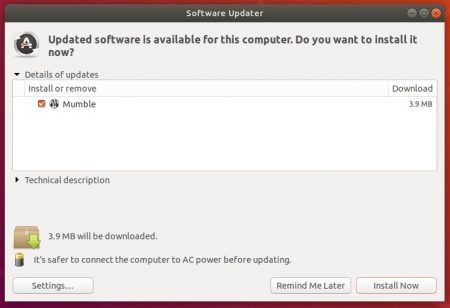
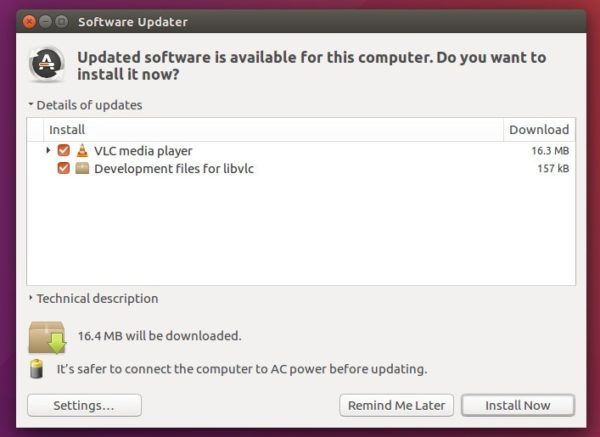
Or open Software Updater and update the software packages:
Uninstall:
You can purge the Ubuntu PPA which also downgrade the installed packages to their stock versions:
sudo apt install ppa-purge && sudo apt install ppa-purge ppa:savoury1/vlc3
Keep an eye when purging the dependency PPA, as it may also remove some media packages.
sudo ppa-purge ppa:savoury1/ffmpeg4
Alternatively, you can just remove the Ubuntu PPAs via commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:savoury1/vlc3
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:savoury1/ffmpeg4
And remove VLC if you want by running command:
sudo apt remove --autoremove vlc