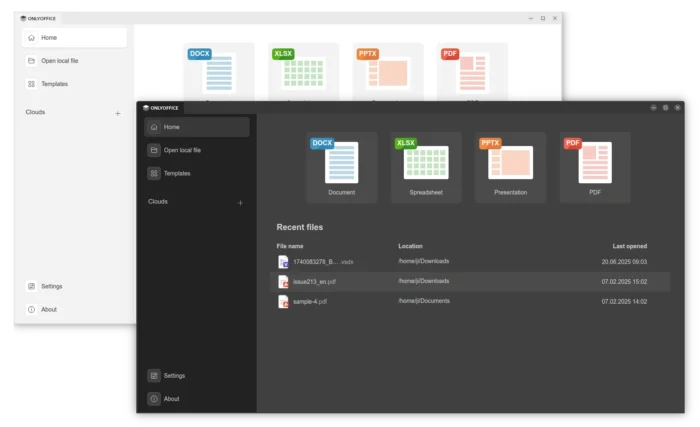
OnlyOffice, the popular free open-source office suite, released new 9.0 version for its offline use desktop editors hours ago.
The new release introduced 2 new themes Modern Light and Modern Dark with redesigned UI elements and icons, as well as redesigned start window with focus on simplicity.