This is a step by step beginner’s guide shows how to manually download & install the new Gnome Adwaita Sans and Adwaita Mono fonts in all current Ubuntu releases.
GNOME introduced new interface font in version 48, named Adwaita Sans and Adwaita Mono. While, Ubuntu does not ship Adwaita fonts in system repository, user can install it manually by following steps.
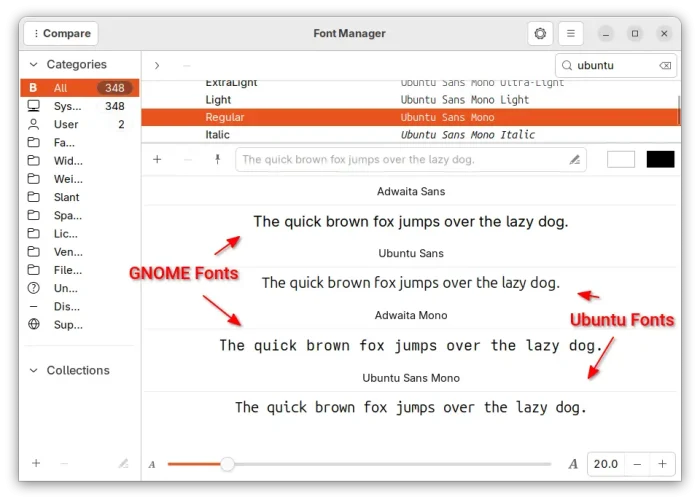
GNOME & Ubuntu Fonts compare in Font Manager
NOT only for Ubuntu, this tutorial should work for most other Linux. And, you may follow this tutorial for manually installing any other fonts.
Step 1: Download Adwaita Fonts
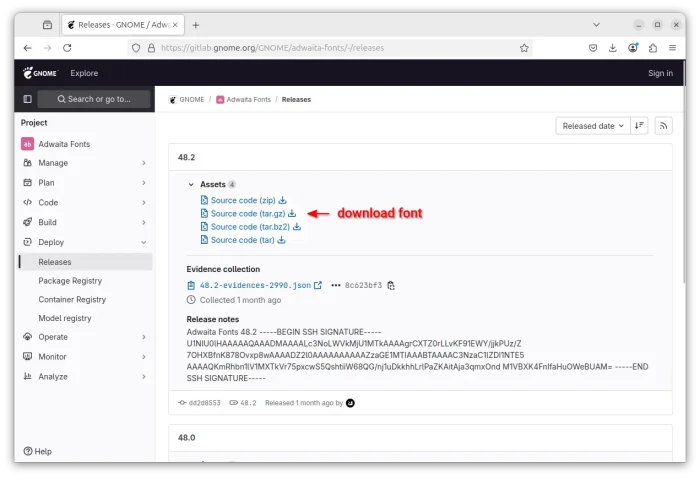
First, download the source code of GNOME Adwaita Fonts from its project page via the link below:
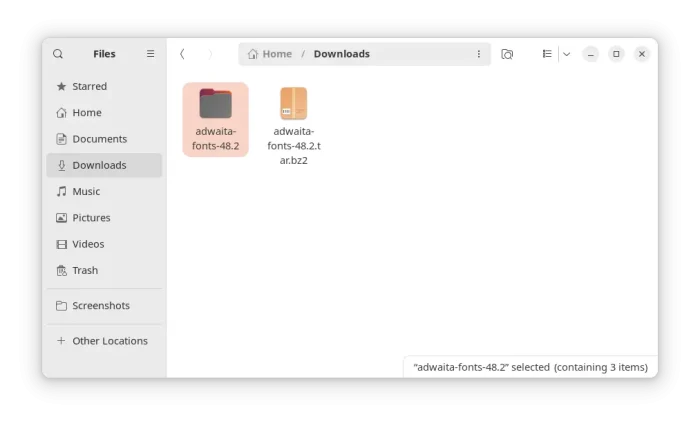
Then, open your Downloads folder and decompress the source tarball. In the extracted folder, you’ll see the font files (.ttf files) under mono and sans sub-folders.
Step 2: Install the Font files
To install manually downloaded fonts in Ubuntu and most other Linux, simply put the .ttf files into one of the following locations:
/usr/share/fonts for fonts that work system-wide (meaning for all users)./usr/local/share/fonts – an alternative system-wide font directory..local/share/fonts or .fonts– for fonts that work for current user only.
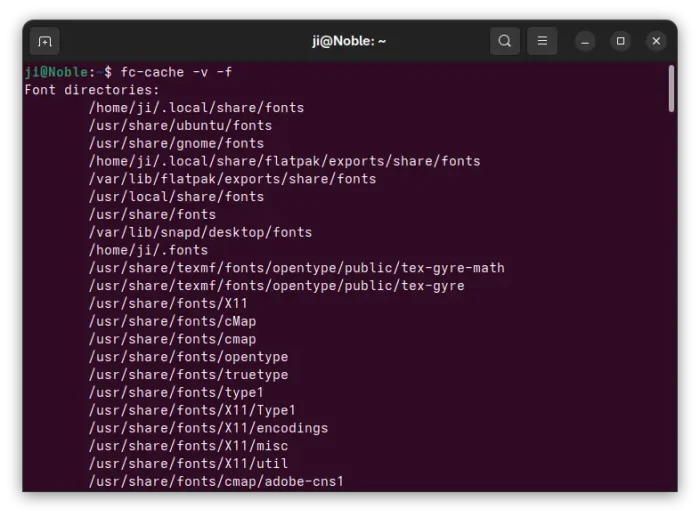
There are as well other locations, such as Ubuntu, GNOME, Flatpak, and Snap specific directories for storing font files. Run command fc-cache -v in terminal to list them all.
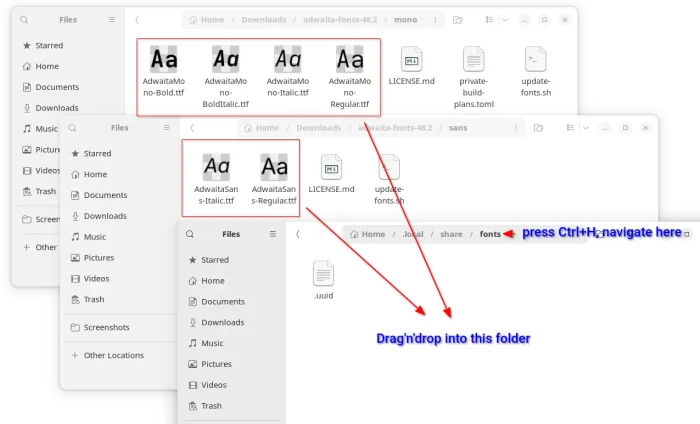
Option 1: Install Adwaita Fonts for current user only
For current user only, open another file manager window, press Ctrl+H to show hidden files/folders, then navigate to .local -> share -> fonts (create if not exist).
Then, drag and drop the .tff font files from the extracted adwaita-fonts folder (mono and sans sub-folders) into that directory.
Finally, press Ctrl+Alt+T to open up a terminal window, and run command to re-generate font cache:
fc-cache -f -v
Option 2: Install Adwaita Fonts for all users
For system wide use, just move the .ttf files into /usr/share/fonts directory (or sub-directory) instead, though you need root permission to do the job.
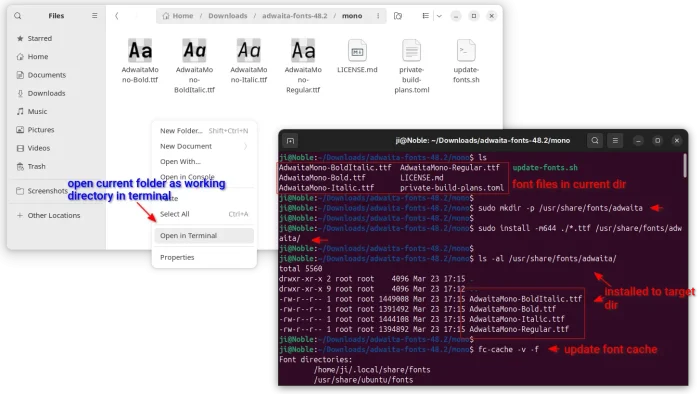
First, open file manager and navigate to the folder that contains the .ttf font files.
- Right-click on blank area and select “Open in Terminal” to open terminal window with that folder as working directory.
- When terminal opens, first run command to create a sub-folder,
adwaita in the case, under target directory:
sudo mkdir -p /usr/share/fonts/adwaita
- Then, run command to install (move and change permission to 644) all
.ttf files from current to the location you just created:
sudo install -m644 ./*.ttf /usr/share/fonts/adwaita
As the .ttf font files are separated into 2 folders (mono and sans sub-folders), you need to open another folder in terminal and re-do the steps above.
When done, also run fc-cache -f -v to apply changes.
Step 3: Apply the New Fonts
After installed font files into target location and updated cache, you may use following tools to apply/change font.
Option 1: Use GNOME Tweaks
For the default GNOME Desktop, GNOME Tweaks (available to install in Ubuntu Software / App Center) tool offers options to do the job in first tab.
NOTE: GNOME Tweaks v46 has bug changing fonts in Ubuntu 24.04, please try other ways instead.
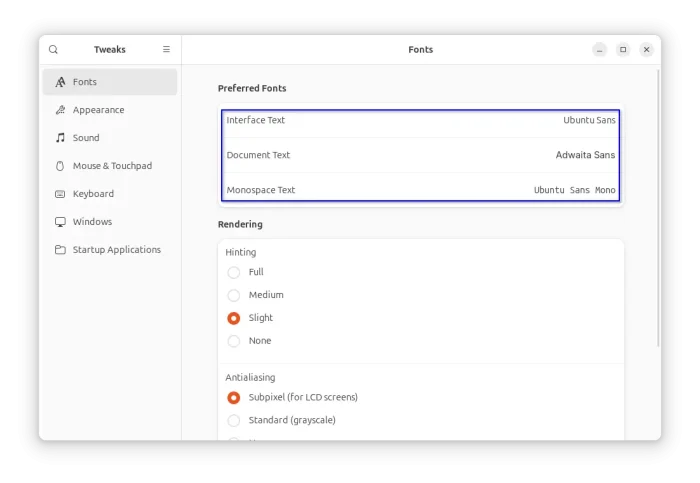
Tips: As you see in the screenshot, there are 3 font options:
- Interface Text – the text font in panels, menus, buttons, Settings, app window titles, etc.
- Monospace Text – font for fixed-width characters in, e.g., terminal, coding, and text editors.
- Document Text – font for displaying document text in an application (GNOME Text editor now use “Monospace Text” font instead).
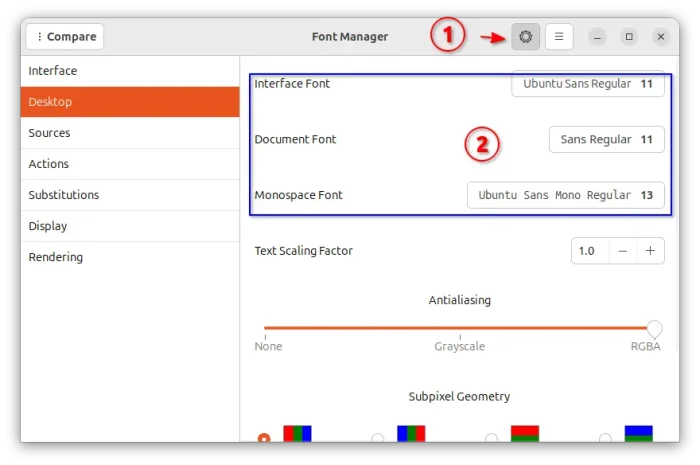
Option 2: Use Font Manager
For non-GNOME desktop users who can’t find out the desktop specific font setting options, “Font Manager” also offers the options the change the fonts.
Simply search for and install the app from Ubuntu Software or App Center, then launch it, and click the setting gear icon in header, finally navigate to “Desktop” in left pane to get the options.
Option 3: Use Dconf Editor
Also for GNOME, the advanced dconf editor tool also provides the options to change fonts. While it also has options to easily reset fonts to default.
First, install Dconf Editor either from AppCenter (or Ubuntu Software) or by running command in terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T):
sudo apt install dconf-editor
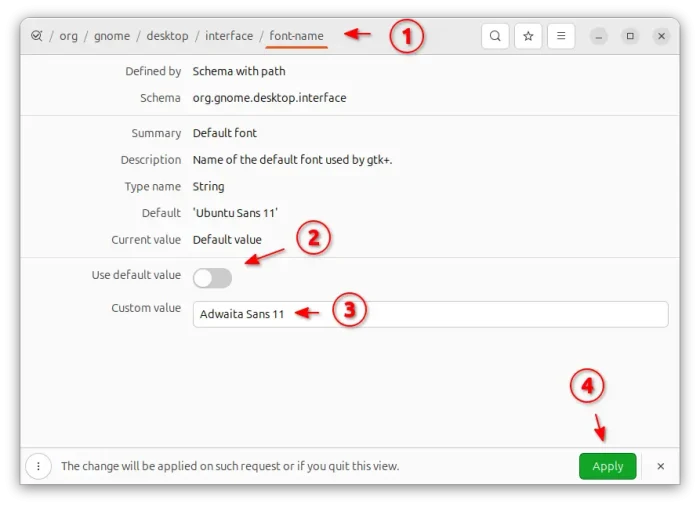
Then, launch Dconf Editor and navigate to org/gnome/desktop/interface. Finally, find out and change the following key values:
- document-font-name – for Document Text.
- font-name – for Interface Text.
- monospace-font-name – for Monospace Text.
For each key, click turn off “Use default value”, then input a custom value Adwaita Sans 11 or Adwaita Mono 11 in the case, finally click the bottom right Apply button.
Option 4: Change fonts from command line (GNOME Only)
For the default GNOME desktop users who are OK with Linux command line, simply press Ctrl+Alt+T to open up a terminal window.
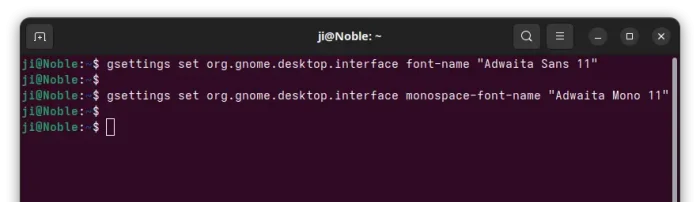
When terminal opens, run the commands below one by one to set Adwaita Fonts:
gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.interface font-name "Adwaita Sans 11"
gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.interface monospace-font-name "Adwaita Mono 11"
gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.interface document-font-name "Adwaita Sans 11"
For choice, you may replace number ’11’ in the command to increase or decrease fonts sizes.
Restore Default Fonts (GNOME Only)
As mentioned above, “Dconf Editor” offer options to reset fonts to default.
Just install & launch the tool, then navigate to org/gnome/desktop/interface, finally click edit each key and turn on “Use default value” option to revert back to default font.
For choice, you may open terminal and run the commands below one by one to restore the fonts:
gsettings reset org.gnome.desktop.interface font-name
gsettings reset org.gnome.desktop.interface monospace-font-name
gsettings reset org.gnome.desktop.interface document-font-name