Gnome Connection Manager is a free and open-source ssh connection manager for gtk+ environments. It features multiple tunnels in tabs and unlimited vertical/horizontal window splitting.
Features:
- Gnome Connection Manager is licensed under the GNU General Public License version 3
- It’s designed in Glade and written in python, so it just need PyGTK to run in any linux environment
- Can store passwords for easy access to hosts
- Supports multiple ssh tunnels for each host
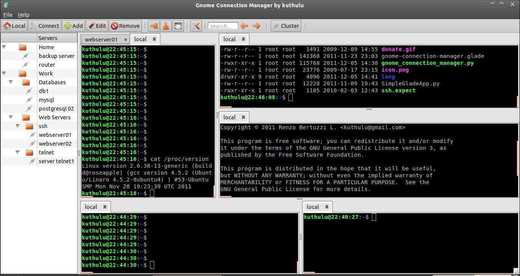
- Unlimited vertical/horizontal window splitting. You can have as many visible consoles as you want
- Drag&Drop tabs between consoles
- Connect to multiple hosts with just one click
- Grouping hosts
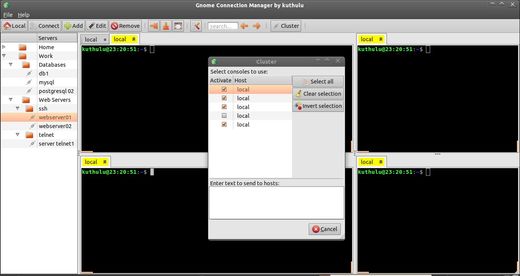
- Cluster mode. Work on several hosts at the same time
- Customizable shortcuts
- Send custom commands to hosts
- It’s free, and the source is included in the download
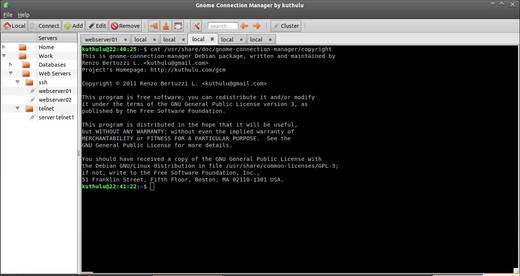
Screenshots:
Install:
The DEB packages for Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint and source code are available in Gnome Connection Manager website.